Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
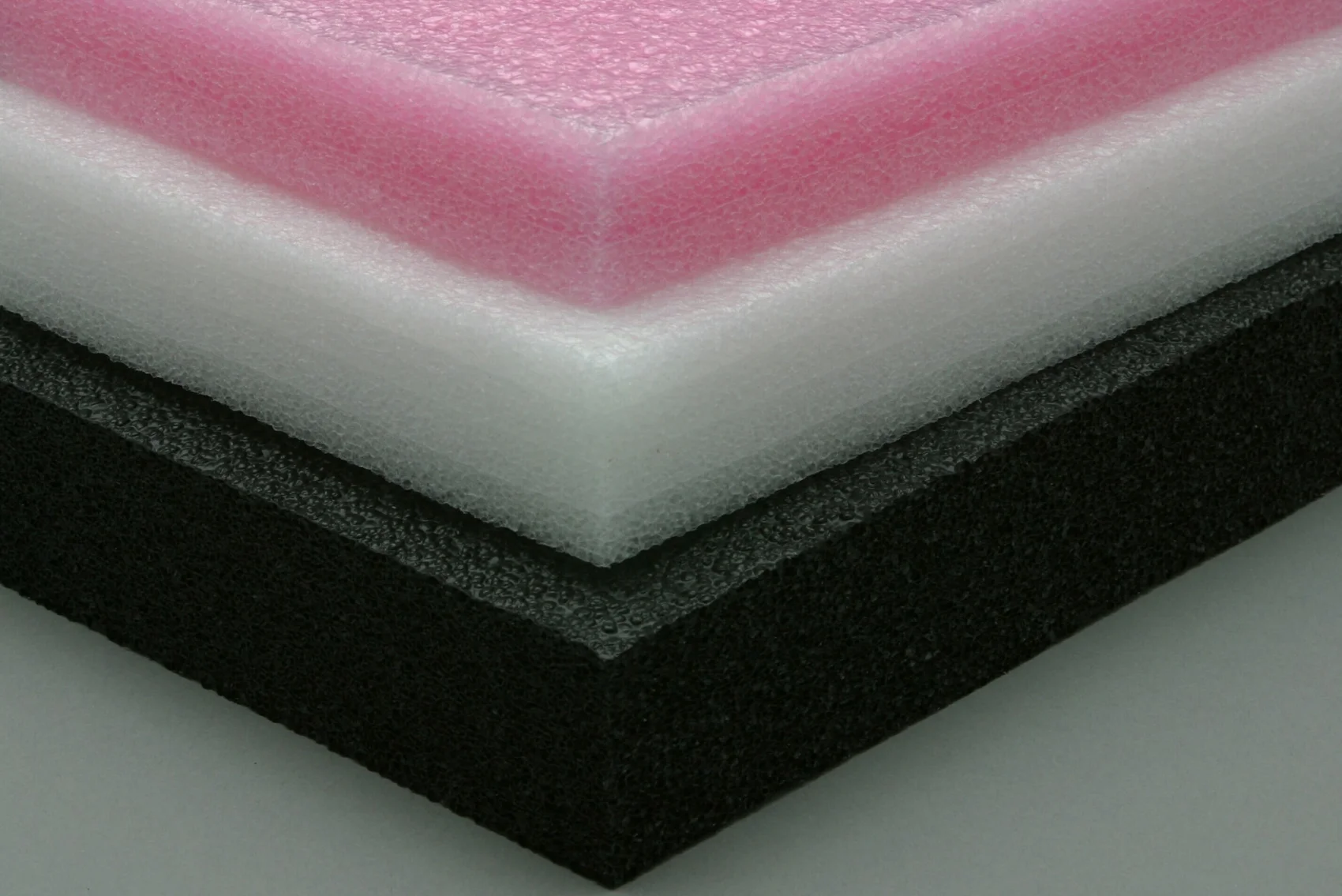
Expanded Polyethylene (EPE) foam has become a staple in a wide range of industries, from packaging to insulation. Known for its flexibility, durability, and lightweight characteristics, EPE foam has proven itself as a versatile and reliable material. This blog delves into the world of EPE foam, examining its properties, safety considerations, recyclability, and comparisons with other types of foam, particularly polyurethane (PU) foam.
EPE foam, or Expanded Polyethylene foam, is a type of plastic foam characterized by its closed-cell structure. This structure gives EPE foam its distinctive qualities, such as flexibility, buoyancy, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. The “expanded” part of EPE refers to the manufacturing process, where polyethylene resin is expanded with a blowing agent, creating a network of interconnected air-filled cells.
The resulting foam is lightweight, flexible, and able to absorb shock and vibration, making it ideal for various applications. EPE foam is commonly used in the following areas:
One of the critical questions surrounding EPE foam is its safety. In general, EPE foam is considered non-hazardous and non-toxic. Unlike some other foam materials, EPE does not release harmful gases or chemicals during manufacturing or use. This characteristic makes it a popular choice for packaging food items and other sensitive products.
However, it’s essential to consider the environmental impact of EPE foam. While it’s not hazardous in terms of human health, the material is not biodegradable. This lack of biodegradability can lead to environmental concerns if EPE foam is not properly recycled or disposed of. Addressing this issue requires a focus on recycling and sustainable practices.
EPE foam’s texture can vary depending on its density and manufacturing process, but it’s generally considered soft and flexible. Its closed-cell structure allows it to compress under pressure and return to its original shape when the pressure is released. This flexibility is one of the reasons EPE foam is so widely used in packaging and cushioning applications.
Despite its softness, EPE foam can be engineered to have varying degrees of firmness, allowing it to be used in more rigid applications. This adaptability makes it a versatile material for a range of industries.
Comparing EPE foam with polyurethane (PU) foam reveals some key differences, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences can help determine which type of foam is best for a specific application.
In summary, EPE foam is typically chosen for its lightweight, flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for packaging and insulation. PU foam, on the other hand, is valued for its cushioning and thermal resistance, often used in furniture and bedding. The choice between EPE and PU foam depends on the specific requirements of the application.
As mentioned earlier, one of the significant concerns with EPE foam is its lack of biodegradability. However, EPE foam can be recycled, helping to mitigate its environmental impact. Recycling EPE foam involves several steps:
Recycling EPE foam helps reduce waste and contributes to a circular economy, where materials are reused and repurposed. However, the recycling process requires specialized equipment and facilities, which can limit its widespread adoption.
EPE foam is a versatile and valuable material used in various industries for its flexibility, durability, and shock absorption. While it is generally non-toxic and safe for use, its lack of biodegradability raises environmental concerns. Recycling EPE foam offers a potential solution to these concerns, contributing to a more sustainable approach to foam usage.
When comparing EPE foam with PU foam, each has its advantages and disadvantages, with the choice depending on the specific needs of the application. As the demand for environmentally conscious practices grows, the focus on EPE foam recycling and sustainable production methods will become increasingly important.